Digital to Analog Conversion

Type of Digital to Analog Conversion

Data rate(Bit rate) : number of bits per second
Signal Rate(baud Rate): Number of signal unit per second S=N*1/r
Bandwidth: signal rate에 비례( FSK제외)
Carrier Signal( or Carrier Frequency): basis 역할을 하는 high frequency signal
Modulation (shift Keying) : Digital information modulates the carrier signal by modifying one or more of characteristics of carreir.
예)
-아날로그 시그널이 시그널 엘리먼트당 4개의 비트를 전송한다. 만약 초당 1000개의 시그널을 전송한다면 이 때 비트rate는?
S=N*1/r공식에 대입 하면 N=Sxr = 1000 x 4 = 4000 bps
- 아날로그 시그널이 8000bps의 bit rate. signal rate= 1000baud. 각 시그널 마다 몇개의 데이터 엘리먼트가 전송 되는가? 얼마나 많은 시그널 레벨이 필요한가?
S=1000, N=8000 에서 r과 L을 구함.

ASK( Amplitude Shift Keying)
- 0과 1로 이루어진 디지털을 다른 진폭들로 변이
- 노이즈에 영향을 많이 받음.
- Binary ASK (BASK, On-Off keying): 2가지 진폭 사용.
bandwidth: (1+d)x S (s는 시그널 레이트, d는 라인 컨디션과 관계된 factor)
- Multilevel AKS : 4,8,6 혹은 더 많은 진폭 사용. ASK만 사용해서 구현 하지 않고 QAM에서 사용됨.


예) Bandwidth가 100kHz이고 200kHz에서 시작해서 300kHz차지. ASK를 사용하여 d=1일 때carrier frequency와 bit rate는?
B=(1+d)S = 2xNx1/r=100kHz 다라서 N=50kHz. carrier frequency는 250kHz
Frequency Shift Keying( FSK)
- 1과 0으로 이루어진 신호를 다른 주파수로 변조
- 노이즈에 영향 받지 않음.
Binary FSK(BFSK): 두개의 carrier frequencies. f1,f2
Bandwidth = (1+d)S+2(f2-f1)
Multilevel FSK: 4,8,16혹은 더 많은 주파수를 사용함.

Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
-1과 0으로 이루어진 신호를 다른 위상으로 변조
- 노이즈 영향 받지 않음. ASK나 FSK보다 흔하게 사용됨.
Binary PSK(BPSK): 두개의 위상 사용. Bandwidth=(1+d)S
Quadrature PSK( QPSK) : use 4 phases


위상과 진폭을 같이 나타내는 그래프.

QAM( Quadrature Amplitude Modulation )
ASK와 PSK를 결합한다. Bandwidth=(1+d)S

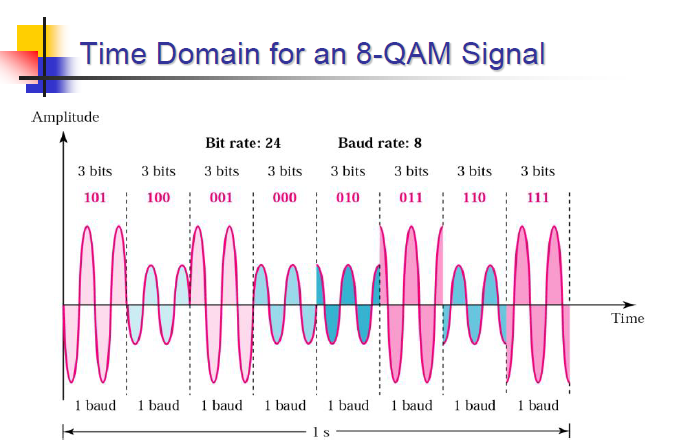
2개의 진폭과 4개의 위상 사용.

Analog to Analog conversion

AM( Amplitude modulation)
Modulate carrier signal so that its amplitude varies with the changing amplitudes of the modulating signal
Bandwidth=2xbandwidth of modulating signal

FM(Frequency Modulation)
Modulation frequency of carrier signal to follow changing voltage level(amplitude) of the modulating signal
Bandwidth= 2(1+b)x bandwidth of modulating signal, b= usually 4

PM(Phase Modulation )
modulation phase of carrier signal to follow changing voltage level(amplitude) of modulating signal
instantaeous change in carrier frequency is proportional to the derivative of amplitude of the modulating signal.
Bandwidth=2(1+b)x bandwidth of modulating signal, b= around 1 for narrowband, 3 for wideband.

